Vision is one of the most critical senses through which individuals interact with their environment. As technology continues to permeate daily life, eye strain and various vision-related ailments have become increasingly prevalent. In light of this growing concern, the practice of eye yoga emerges as a compelling alternative for those seeking to improve their visual health. Eye yoga encompasses a series of exercises designed to strengthen ocular muscles, enhance focus, and promote overall eye well-being. This article delves into various techniques of eye yoga, their physiological underpinnings, and the benefits they may confer.
Understanding the mechanics of eye function is pivotal for comprehending how eye yoga can be beneficial. The human eye is a complex organ consisting of numerous components, including the cornea, lens, and retina, all contributing to visual acuity. Muscles surrounding the eyeball facilitate movement and focus, which can become fatigued due to prolonged usage of electronic devices. Eye yoga exercises target these muscles, providing relief from strain while fostering enhanced functionality. By engaging in a regular routine, individuals may mitigate symptoms associated with digital eye strain and potentially bolster their overall eye health.
Historically rooted in ancient practices, yoga has been recognized for its holistic benefits, including physical, mental, and emotional enhancement. The essence of eye yoga aligns with these principles, offering a specialized approach to tackling contemporary visual ailments. As the demand for non-invasive remedies increases, eye yoga stands out by combining ocular exercises with the meditative aspects of traditional yoga, promoting greater mindfulness and relaxation during sessions.
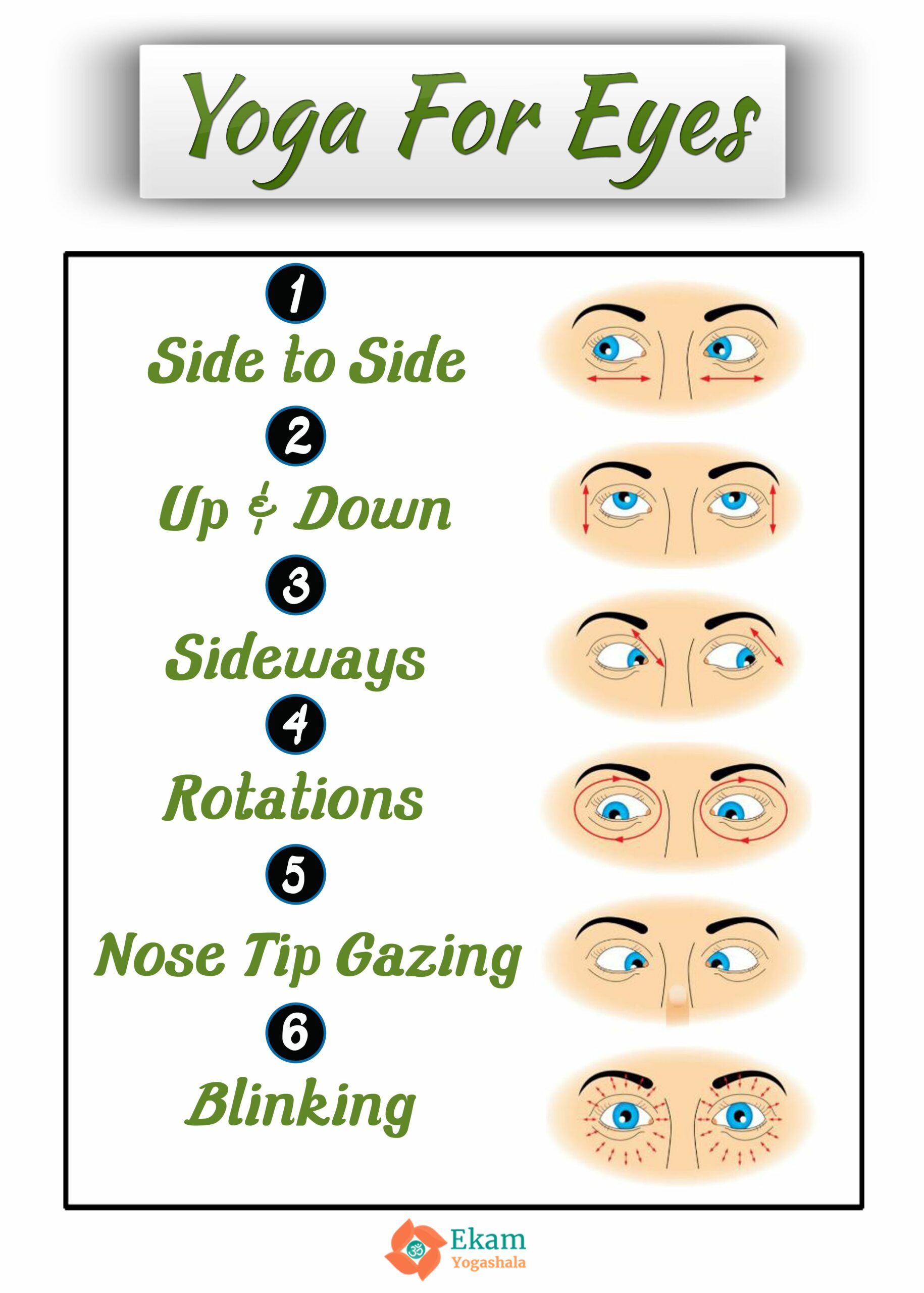
Engaging in eye yoga does not require specialized equipment or an extensive time commitment, making it accessible for all individuals. A common framework includes exercises that enhance flexibility, coordination, and strength in the eye muscles. Below, we explore a variety of eye yoga techniques, categorizing them based on their focus and intended outcomes.
Eye Relaxation Techniques
One key component of eye yoga is relaxation. The following practices emphasize unwinding the ocular muscles and alleviating tension:
Palming: This technique is fundamental to eye relaxation. It involves rubbing the palms together to generate warmth and gently cupping them over the closed eyes to block out light. While in this position, practitioners can take deep breaths, allowing the mind and body to release stress. This simple exercise, lasting between one to five minutes, can significantly diminish feelings of fatigue and stress associated with prolonged screen time.
Blinking Exercises: Regular blinking is essential for maintaining eye moisture and comfort. Many individuals, when focused on screens, tend to blink less frequently. A recommended exercise is to consciously blink every four seconds for a period of thirty seconds. Follow this with a brief moment of complete closure to allow the eyes to rest. Repeating this process several times throughout the day can help alleviate dryness and discomfort.
Gazing Exercises
Incorporating focal changes into eye yoga aids in improving visual acuity. These exercises shift focus between near and distant objects, helping to strengthen the eye muscles:
20-20-20 Rule: To mitigate fatigue during prolonged screen use, the 20-20-20 rule is beneficial. Every 20 minutes, users should aim to look at an object approximately 20 feet away for 20 seconds. This practice facilitates a shift in focus, allowing eye muscles to relax while reducing visual strain.
Near-Far Focus: This exercise requires individuals to select two objects—one nearby and one distant. Alternating focus between the two objects can enhance flexibility and response time in ocular muscles. Engaging in this practice for about five minutes is advisable. It serves to reinforce the visual system’s adaptability, fostering better overall eyesight.
Strengthening Techniques
For those seeking to strengthen their ocular muscles, specific exercises target muscle tonicity and endurance:
Rolling Eyes: Eye rolling can be an invigorating practice. By looking in a circular motion—first clockwise, then counterclockwise—individuals can engage all surrounding muscles. This exercise, performed for 30 seconds in each direction, enhances muscle coordination and helps maintain elasticity.
Convergence Exercises: Convergence is the process where both eyes move toward each other to focus on a near object. To perform this, hold a pencil or a finger at arm’s length and slowly move it towards the nose, maintaining focus on the object. Repeat this process ten times. Enhancing convergence can aid in improving the ability to focus on nearby objects, an essential skill in an increasingly screen-based world.
Mindful Integration of Eye Yoga
Incorporating mindfulness into eye yoga magnifies its potential benefits. Mindfulness encourages practitioners to be present, fostering a deeper connection with their bodily sensations:
Breath Awareness: Synchronizing breath with eye exercises can elevate the mindfulness experience. For instance, coordinating deep inhalations with eye rolling or focusing exercises can cultivate a tranquil state conducive to relaxation.
Visualization Techniques: During practices such as palming, visualizing serene landscapes or calming imagery can enhance the relaxation response. This mental incorporation not only amplifies relaxation but also combines the power of the mind in promoting visual health.
Long-term Benefits and Recommendations
Research indicates that the adoption of eye yoga strategies may yield extensive long-term benefits. Enhanced muscle strength, improved focus, and reduced discomfort are among the most reported advantages. However, individual experiences will vary. While eye yoga can serve as an adjunct to traditional methods, it should not replace professional advice from healthcare providers, especially for individuals experiencing significant visual impairments.
Consistency is paramount for reaping the benefits of eye yoga. Practitioners are encouraged to integrate these exercises into daily routines, perhaps commencing or concluding their day with a focused session. Adaptability is key; individuals should modify exercises according to their comfort levels and daily circumstances, ensuring that eye yoga remains a sustainable practice.
Consideration for practitioners must also extend to broader lifestyle choices that affect eye health. Sufficient hydration, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants (such as vitamins A, C, and E), and regular eye examinations are essential in maintaining and strengthening visual acuity over time.
In conclusion, the realm of eye yoga represents a multifaceted approach to enhancing visual health and comfort. By emphasizing relaxation, strengthening exercises, and mindful engagement, individuals can effectively combat the challenges presented by modern life while fostering a deeper connection with their eyesight. Ultimately, while eye yoga may not serve as a panacea, it offers a plethora of benefits that merit incorporation into daily routines and broader discussions on ocular health.